“`html
Understanding Keto Enol Tautomerism
The Basics of Keto Enol Tautomerism
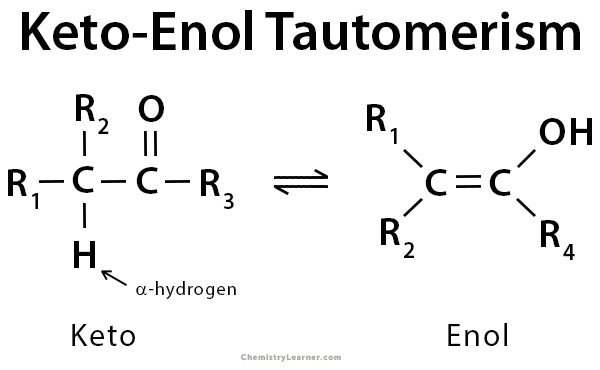
Keto enol tautomerism is a fascinating chemical phenomenon that involves the interconversion between two structural forms: the **keto form** and the **enol form**. In understanding this concept, it’s crucial to grasp the nature of **tautomeric equilibrium**—a dynamic process where these two isomers rapidly transform into one another, typically influenced by factors like solvent, temperature, and pH. The keto form generally features a carbonyl group (C=O), while the enol form exhibits a C=C double bond coupled with a hydroxyl group (OH). This differentiation plays a critical role in **reaction pathways** among **carbonyl compounds**, especially within organic synthesis. Tautomerism is not just an academic concept; it has significant practical applications in drug design and biochemical processes. Familiarity with tautomeric shifts is essential for understanding various chemical reactions and stability characteristics of compounds.
Key Differences Between Keto and Enol Forms
The **keto form** typically demonstrates greater thermodynamic stability compared to its **enol form**, yet in specific contexts, such as catalytic conditions, enolic forms may dominate due to **kinetic factors**. For instance, in the tautomerism of simple ketones, the keto form, which is often favored, can be converted into the enol by an acid-catalyzed or base-catalyzed reaction. This stability shift directly influences the **reaction kinetics** and the overall reactivity of the compound in diverse chemical reactions, such as nucleophilic attack and electrophilic addition. The relative stabilities of both forms can be influenced by the presence of substituents around the carbon chain, showcasing the complexity and importance of understanding keto enol tautomerism in organic chemistry.
Mechanisms of Tautomerization
The mechanisms behind **tautomerization** can be categorized into two predominant pathways: acid-catalyzed and base-catalyzed tautomerization. In acid-catalyzed tautomerization, the process typically begins with protonation of the carbonyl oxygen, leading to the formation of a carbocation intermediate. This step is crucial as it increases the electrophilicity of the carbon atom and enables the formation of the enol through proton transfer. Conversely, **base-catalyzed tautomerization** involves the deprotonation of the alcohol proton in the enol form, with subsequent **nucleophilic attack** on the carbonyl carbon. Each pathway emphasizes the role of **hydrogen bonding** and **proton transfer**, pivotal in influencing the equilibrium state of the reactions, thus laying the groundwork for further explorations in **chemical synthesis** and mechanism analysis.
Tautomeric Equilibrium and Its Influence
The understanding of **tautomeric equilibrium** is vital for grasping the reactivity patterns of various organic compounds. This equilibrium dictates the ratio of keto to enol forms in a molecule, which can vary due to environmental factors such as the type of solvent utilized. For instance, protic solvents may stabilize the tautomeric form by favoring hydrogen bonding interactions, thereby affecting reaction outcomes. Moreover, the influence of substituents at various positions within the carbon chain also plays a role, altering the relative stabilities of both tautomers. Hence, identifying the conditions that impact tautomeric ratios can lead to optimized **reaction conditions** in organic synthesis and serve as a guide for predicting behavior in **synthetic applications**.
Role of Solvents in Tautomerization
Solvents significantly influence tautomeric equilibria by stabilizing one form over the other through various interactions. For example, when utilizing polar protic solvents, such as water or alcohol, the solvated environment can enhance the stability of the enol form through effective hydrogen bonding. In contrast, polar aprotic solvents may influence tautomerization differently, often leading to distinct pathways. Understanding how to manipulate solvent systems allows chemists to control the **keto-enol conversion** effectively. Practical applications of this can be observed in the synthesis of derived products where specific tautomerization states are desired. Awareness of solvent-selective engagements facilitates enhanced outcome predictability and is an essential tool in organic synthesis strategy formulation.
Tautomerism in Biological Systems
Beyond theoretical constructs and laboratory applications, **tautomerism in biological systems** holds profound significance. Many biochemical processes rely on the tautomeric forms of compounds, especially in enzyme activities and metabolic pathways. For example, uracil can exist in different tautomeric forms that significantly impact its role in nucleic acid metabolism. Understanding these pathways through reaction mechanisms elucidates essential biochemical principles and allows for further insights into drug design and development. Analyzing the **stability of enol forms** also gives researchers a comparative basis for assessing therapeutic efficacy and the potential roles of natural products containing keto-enol tautomeric interchange.
Applications of Keto Enol Tautomerism in Organic Synthesis
Incorporating knowledge of **keto enol tautomerism** promotes innovative strategies in organic synthesis. Recognizing when and how to exploit tautomeric conversions can lead to enhanced synthesis processes and improved productivity in generating useful compounds. Understanding the principles behind the **synthesis of enolates** contributes directly to evaluation methodologies suited for effective reaction design. Moreover, the development of methodologies utilizing tautomerization is revealing impressive advances across the medicinal chemistry landscape, emphasizing the need to closely analyze structures, reactivity patterns, and target functionalities within drug design frameworks. By leveraging known tautomeric pathways, chemists can streamline syntheses while optimizing the curing properties of compounds for extensive utility in therapeutic fields.
Keto-Enol Interconversion: Synthetic Applications
The **keto-enol interconversion** is pivotal in many synthesis applications, particularly in the formation of intermediates necessary for further transformations. One prominent example of this is the formation of enolates, which serve as vital nucleophiles in C-C bond formation through alkylation or aldol reactions. Therefore, mastering the enolization process is critical for chemists aiming to create complex molecular architectures. Additionally, exploring **thermodynamic stability** through synthetic outcomes not only enhances yields but can also inform the optimization of conditions for known transformations. A deliberate evaluation of reaction coordinates and conditions reduces trial and error and fosters rapid developments in synthetic methodologies.
Further Implications of Tautomerism in Organic Chemistry
The implications of tautomerism extend deeply into various branches of **theoretical chemistry** and practical applications. Studying tautomeric shifts enlightens the paths taken in reaction mechanisms and influences how researchers visualize chemical reactivity. This practice translates well into educational resources, as effectively teaching tautomerism enables future chemists to have a thorough understanding of underlying principles. Furthermore, advancements in **computational chemistry tools** provide pathways for predicting and optimizing cyclic tautomeric forms, paving the way towards the design of even more robust synthetic strategies. As the field progresses, tautomerism will undoubtedly continue to reveal new insights and innovations relevant to industry practices.
Key Takeaways
- Keto enol tautomerism plays a crucial role in many organic reactions through the interconversion of distinct forms.
- The reaction kinetics and thermodynamic stability drive the equilibrium between tautomers, influencing synthetic outcomes.
- Understanding the roles of solvents and substitution is vital for exploiting tautomerization in chemical processes.
- Tautomerism finds relevance in biological systems and can be leveraged in drug design and medicinal chemistry.
FAQ
1. What are the key characteristics of keto and enol forms?
The **keto form** features a carbonyl group (C=O) and is generally more stable than the **enol form**, which displays a C=C double bond alongside a hydroxyl group (OH). This fundamental difference influences their reactivity in various chemical reactions and their stability under different conditions.
2. How does solvent choice affect tautomeric equilibrium?
Solvent selection significantly impacts the **tautomeric equilibrium** by stabilizing one form over another. Protic solvents tend to stabilize enols through hydrogen bonding, while polar aprotic solvents may promote the stability of ketones. Hence, choosing the appropriate solvent can optimize synthetic outcomes.
3. Can you explain the mechanisms of tautomerization?
Tautomerization can occur via two main mechanisms: acid-catalyzed, where protonation of the keto form leads to the enol form, and base-catalyzed, where deprotonation of the enol leads back to the keto form. Understanding these mechanisms is key to manipulating reaction pathways in organic chemistry.
4. What role does tautomerism play in organic synthesis?
Tautomerism is significant in organic synthesis, particularly in the **synthesis of enolates**, which serve as important intermediates. Recognizing when to exploit tautomeric conversions allows chemists to develop effective synthetic strategies for creating diverse organic compounds.
5. Why is tautomerism important in biological systems?
Tautomerism plays a critical role in biological systems, influencing enzyme activities and metabolic processes. For example, variations in nucleic acid bases due to tautomeric forms can significantly affect genetic information fidelity and biological function. Such processes underline the relevance of understanding tautomerism in biochemistry.
6. What are some practical applications of tautomerism in drug design?
In drug design, understanding tautomerism can optimize the reactivity and stability of pharmaceutical compounds. Identifying which tautomer is predominant under physiological conditions can guide researchers in selecting the most effective molecular candidates for therapeutic interventions.
7. How do temperature and pH influence tautomerism?
Temperature and pH are pivotal in determining the ratio of keto and enol forms. Changes in temperature can affect reaction kinetics, while pH influences the protonation states of the forms, thereby shifting the **tautomeric equilibrium** towards the more stable form in accordance with prevailing conditions.
“`